steps for deploying docker to GKE
First we have to set some env variables. like these:
$ export PROJECT_ID=blissful-canyon-363***
$ export REGION=us-west1
After that we setup gcloud's project ID and create a docker repo.
$ gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
$ gcloud artifacts repositories create hello-repo \
--repository-format=docker \
--location=$REGION \
--description="Docker repository"
Before we push container to that repo, we want to build an docker image. Run this command:
$ git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/kubernetes-engine-samples
$ cd kubernetes-engine-samples/hello-app
$ docker build -t ${REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/${PROJECT_ID}/hello-repo/hello-app:v1 .
For now we have got an image whose tag is ${REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/${PROJECT_ID}/hello-repo/hello-app:v1.
Get auth from the repo (like `dockder login`):
$ gcloud auth configure-docker ${REGION}-docker.pkg.dev
Push image to that repo:
$ docker push ${REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/${PROJECT_ID}/hello-repo/hello-app:v1
Now images in repo are prepared. We have to create a k8s cluster for running the image.
Setup k8s cluster to Autopilot and create one:
$ gcloud config set compute/region ${REGION}
$ gcloud container clusters create-auto hello-cluster
Running the following command will get the output:
$ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
gk3-hello-cluster-default-pool-c4c5959a-4pbd Ready <none> 24m v1.22.12-gke.2300
gk3-hello-cluster-default-pool-d3b8c13d-9q98 Ready <none> 19m v1.22.12-gke.2300
gk3-hello-cluster-default-pool-d3b8c13d-n7df Ready <none> 24m v1.22.12-gke.2300
Since the cluster has been created we have to create a Deployment on it.
Run this command to get credentials from the created cluster:
$ gcloud container clusters get-credentials hello-cluster
Create a deployment to run the image in docker repo:
$ kubectl create deployment hello-app --image=${REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/${PROJECT_ID}/hello-repo/hello-app:v1
Create the base replicas to 3:
$ kubectl scale deployment hello-app --replicas=3
Setup auto-scaling policy from min 1 to max 5:
$ kubectl autoscale deployment hello-app --cpu-percent=80 --min=1 --max=5
Finally we check the pods that were already deployed.
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hello-app-7d989d7dcc-l5jsh 1/1 Running 0 25m
But how can we access the docker service? Here we need to expose the cluster as a service.
Run this command to expose the service:
$ kubectl expose deployment hello-app --name=hello-app-service --type=LoadBalancer --port 80 --target-port 8080
It maps the port from internal 8080 to external 80 and generates a public IP via LoadBalancer server.
Run this command to get the service IP:
$ kubectl get service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
hello-app-service LoadBalancer 10.104.2.106 34.82.180.103 80:32221/TCP 6m7s
Copy the external IP to browser as input and you will see the output of that docker service.
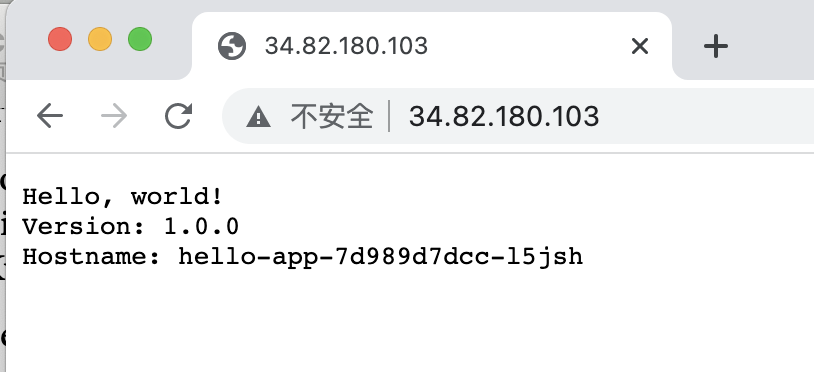
Until now all done well.